Amazon Web Services (AWS) Cloud9
Table of contents
- Notice
- What is AWS Cloud9?
- How to create an IAM role for an AWS cloud9 workspace
- How to create an AWS cloud9
- How to set configurations of the AWS cloud9
- How to install utilities for developing the Amazon EKS on the AWS cloud9
- How to create and import a SSH key
- How to create an AWS KMS custom managed key (CMK)
- How to resize the Elastic Block Storage (EBS) volume
- How to fix error
- Reference
1. Notice
- A guide for setting the Amazon Web Services (AWS) Cloud9
- The name of region is Asia Pacific (Seoul) and the corresponding code is ap-northeast-2 [1].
- I recommend that you should ignore the commented instructions with an octothorpe, #.
- I recommend that you should fill in the appropriate letters between the parentheses, <>.
2. What is AWS Cloud9?
AWS Cloud9 is a cloud-based integrated development environment (IDE) that lets you write, run, and debug your code with just a browser. It includes a code editor, debugger, and terminal. Cloud9 comes prepackaged with essential tools for popular programming languages, including JavaScript, Python, PHP, and more, so you don’t need to install files or configure your development machine to start new projects [2].
3. How to create an IAM role for an AWS cloud9 workspace
You can create an Identity and Access Management (IAM) role on AWS IAM management console - Role. Fig. 1 shows how to create an IAM role and result of the created IAM role. You can refer to the AWS EKS workshop guide to create an IAM role, Create an IAM role fol your workspace.
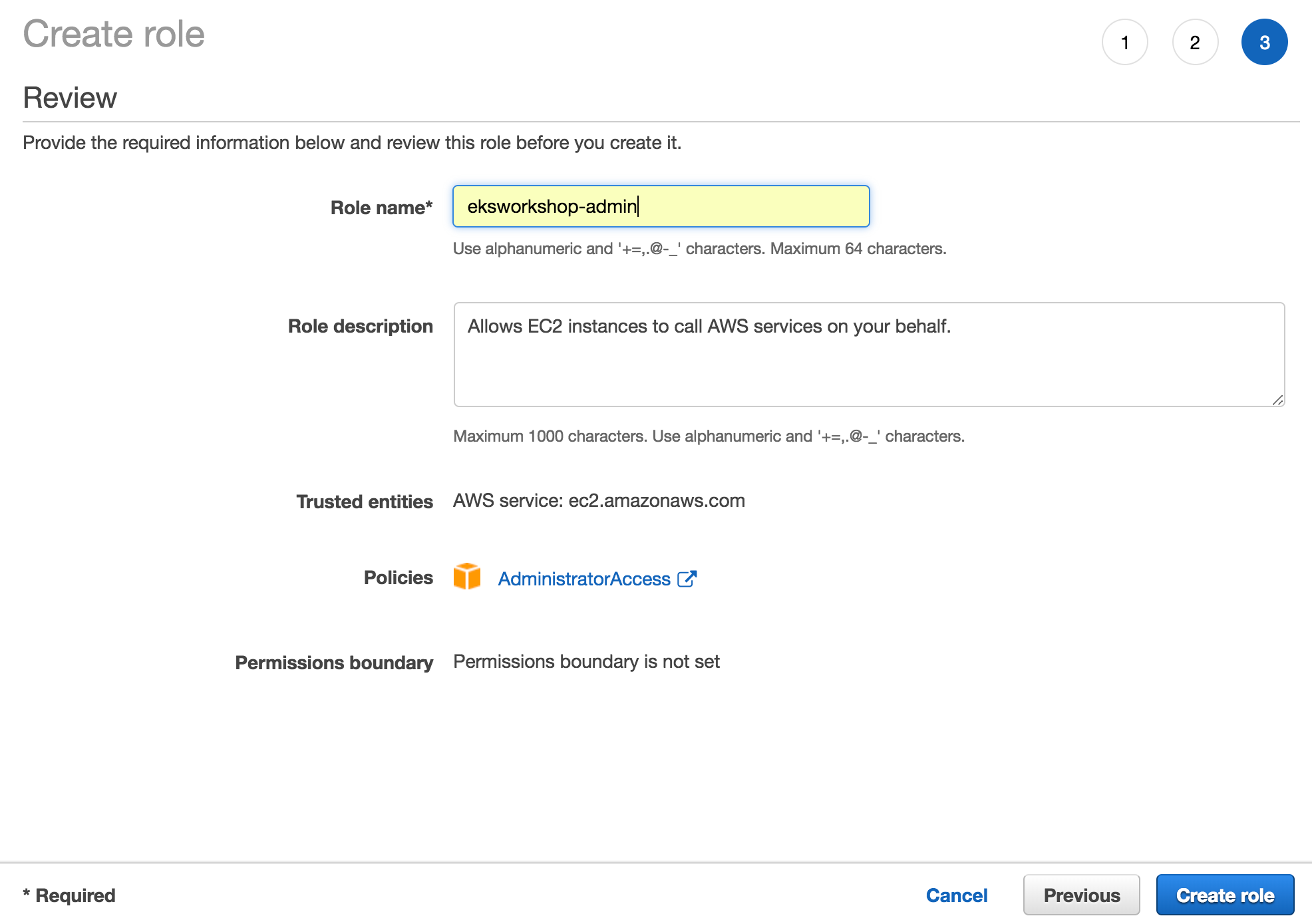
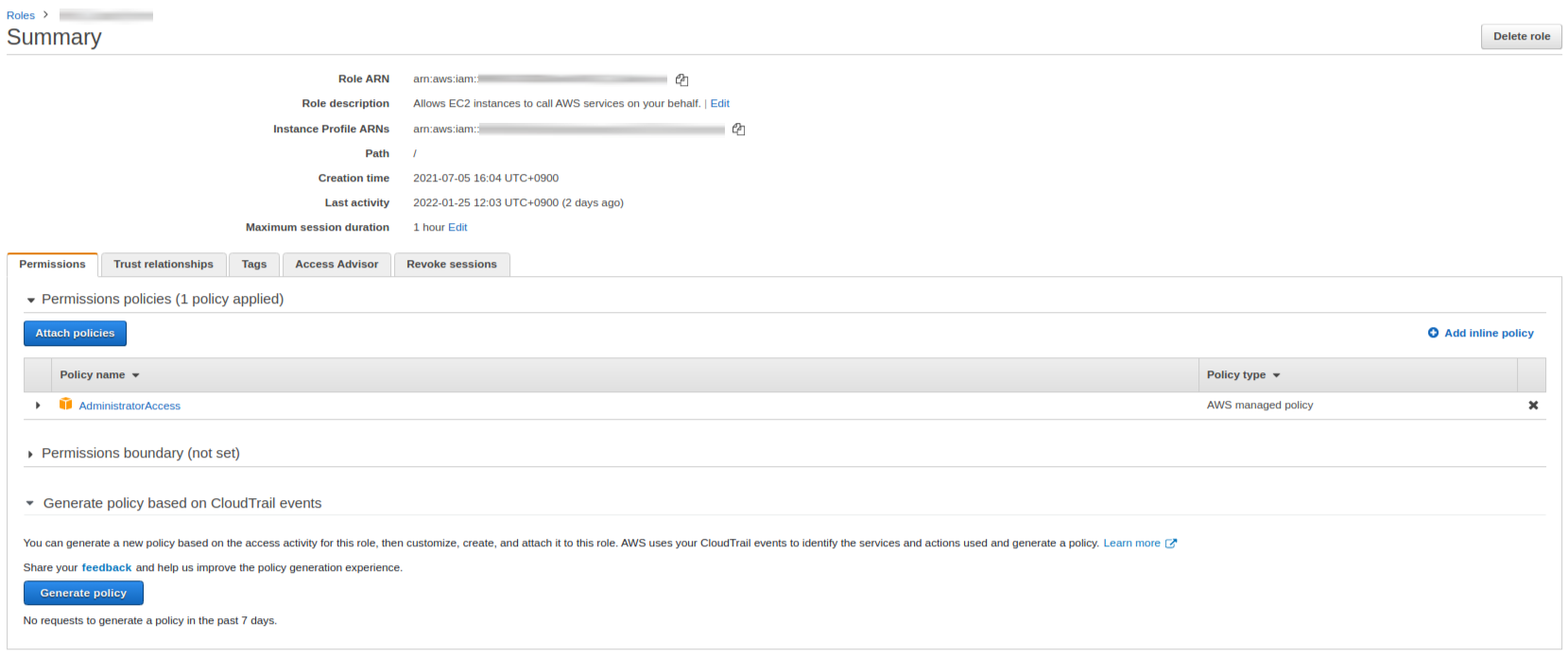
4. How to create an AWS cloud9
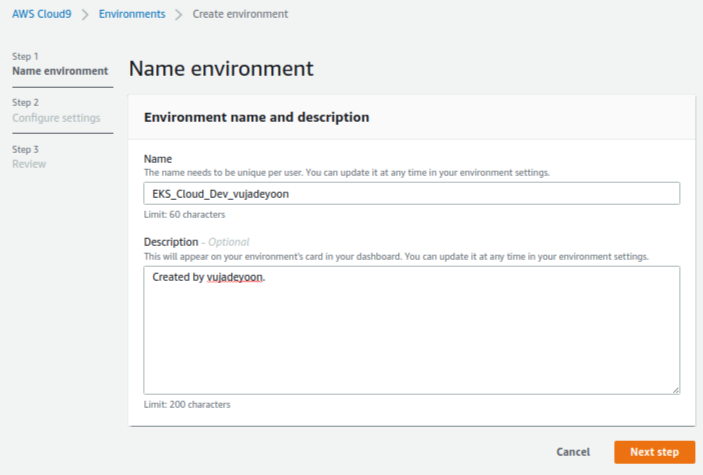
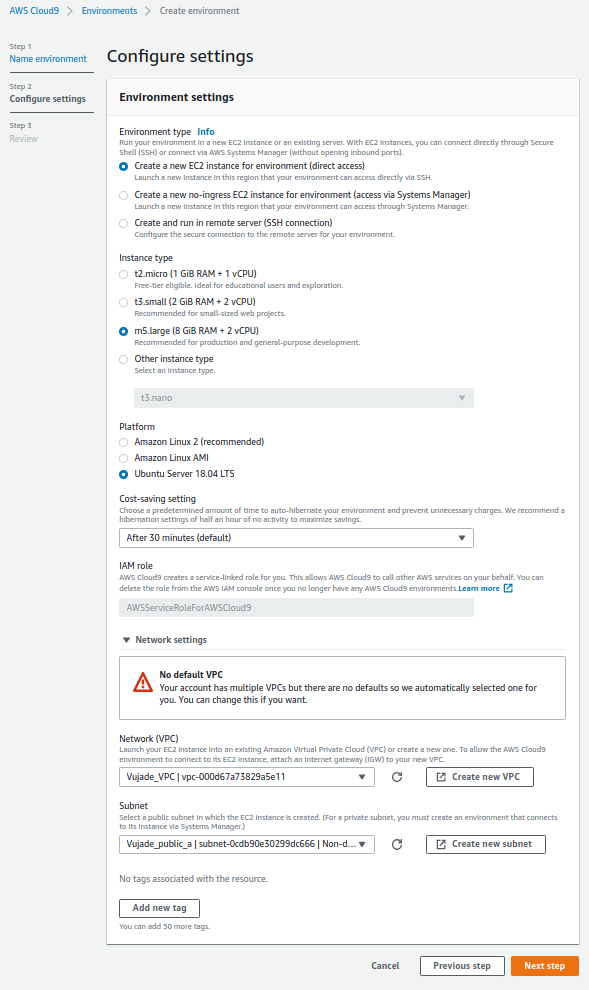
You can create an AWS cloud9 as shown in Fig. 2. There are two important things as follows: i) I recommend that you should select a m5.large (8 GiB RAM + 2vCPU) instance among instance types; ii) You should select a public subnet. The options for creating the AWS cloud9 as follows:
| No. | Environment type | Instance type | Platform | Cost-saving setting | Network (VPC) | Subnet | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Create a new EC2 instance for environment (direct access) | m5.large (8 GiB RAM + 2vCPU) | Ubuntu Server 18.04 LTS | After 30 minutes (default) | Vujade_VPC | Vujade_public_a |
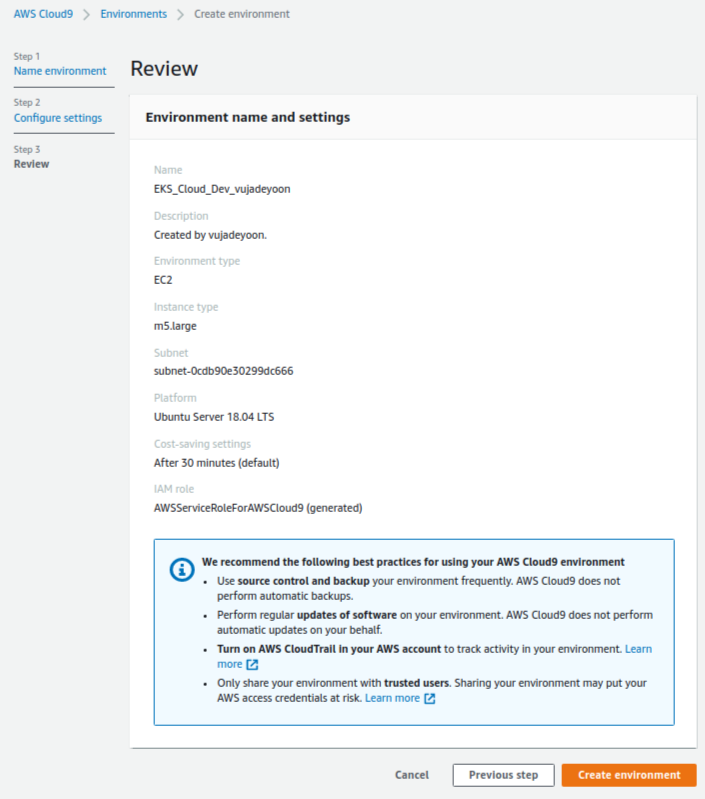
5. How to set configurations of the AWS cloud9
You should set two configurations of the AWS cloud: i) Attaching the IAM role; ii) Disabling AWS managed temporary credentials.
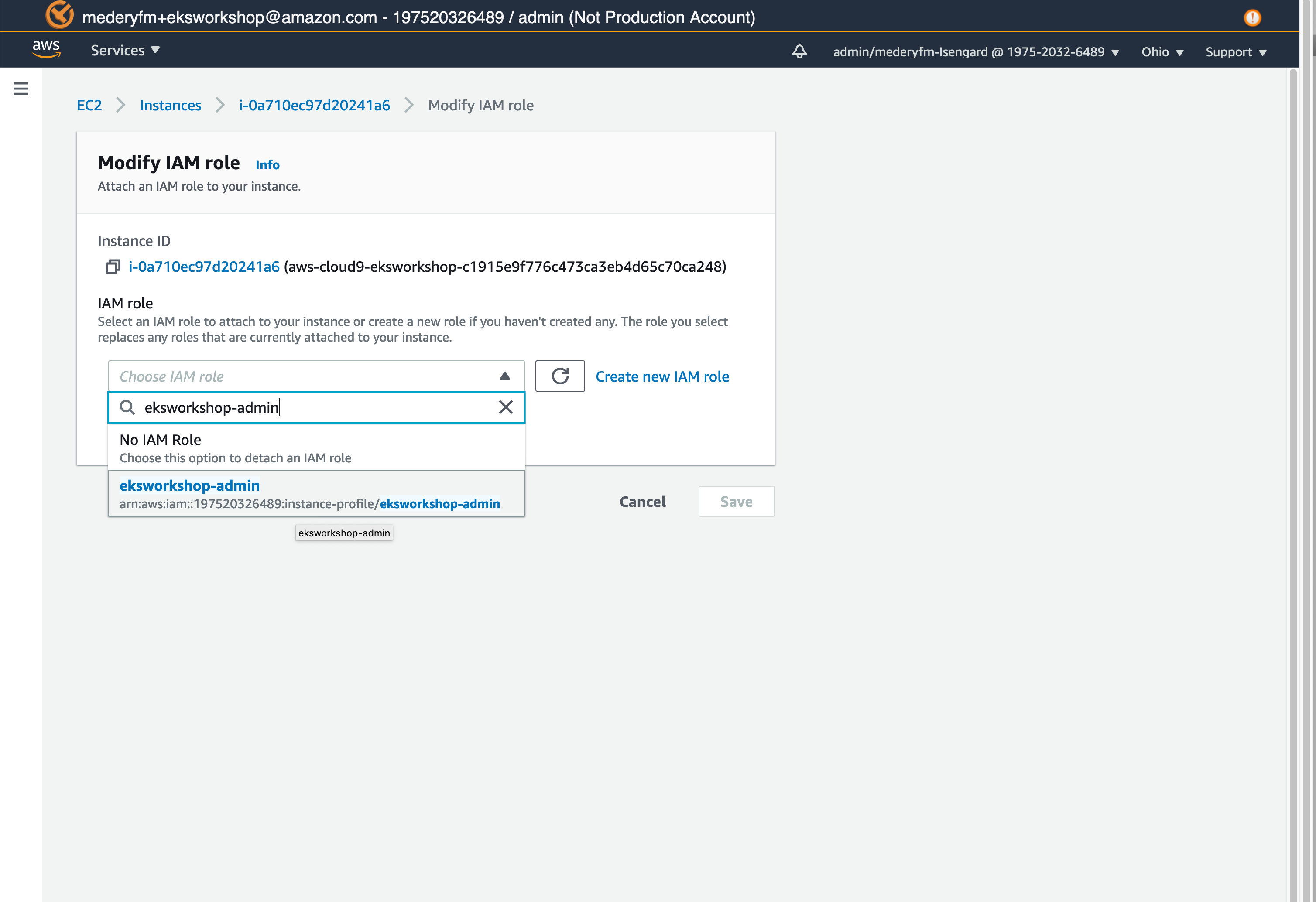
- Attaching the IAM role
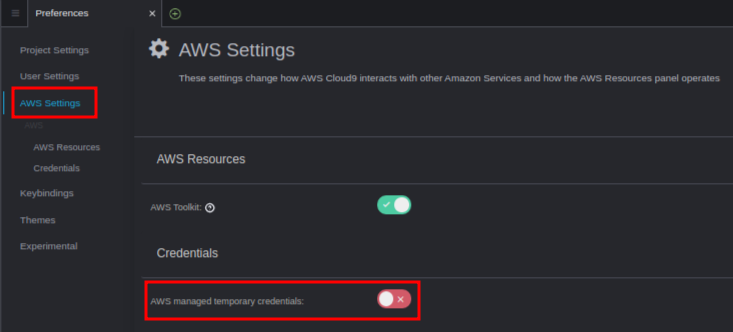
You can attach the IAM role which is created in the Section 3. How to create an IAM role for an AWS cloud9 workspace as shown in Fig. 3. You can refer to the AWS EKS workshop guide, Attach the IAM role to your workspace. - Disabling AWS managed temporary credentials
You can disable the AWS managed temporary credentials as shown in Fig. 4.
6. How to install utilities for developing the Amazon EKS on the AWS cloud9
You can easily install utilities for developing the Amazon EKS on the AWS cloud9 by executing bash_install_utils_eks.sh. Please note that you should type a correct the name of the IAM role which is created in the Section 3. How to create an IAM role for an AWS cloud9 workspace. You can refer to the official guides [3]–[7].
1 $ bash bash_install_utils_eks.sh <NAME_IAM_ROLE>
bash_install_utils_eks.sh
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
# Dveloper: vujadeyoon
# Email: vujadeyoon@gmail.com
# Github: https://github.com/vujadeyoon
# Personal website: https://vujadeyoon.github.io
#
# Title: bash_install_utils_eks.sh
# Description: A bash script to install utilities for EKS.
#
#
# Set name of the created IAM role for the AWS cloud9.
NAME_IAM_ROLE=$1
#
#
# Installing utilities
echo '============================================'
echo 'Utilities'
echo '============================================'
sudo apt-get install -y yum
sudo snap install yq
sudo apt-get install -y gettext bash-completion moreutils jq
sudo pip install --upgrade awscli && hash -r
#
#
# Environmnet configuration
echo '============================================'
echo 'Environment configuration'
echo '============================================'
export ACCOUNT_ID=$(aws sts get-caller-identity --output text --query Account)
export AWS_REGION=$(curl -s 169.254.169.254/latest/dynamic/instance-identity/document | jq -r '.region')
test -n "$AWS_REGION" && echo AWS_REGION is "$AWS_REGION" || echo AWS_REGION is not set
echo "export ACCOUNT_ID=${ACCOUNT_ID}" | tee -a ~/.bash_profile
echo "export AWS_REGION=${AWS_REGION}" | tee -a ~/.bash_profile
aws configure set default.region ${AWS_REGION}
aws configure get default.region
aws sts get-caller-identity --query Arn | grep ${NAME_IAM_ROLE} -q && echo "IAM role valid" || echo "IAM role NOT valid"
#
#
# Installing Elastic Load Balancing (ELB)
echo '============================================'
echo 'Elastic Load Balancing (ELB)'
echo '============================================'
aws iam get-role --role-name "AWSServiceRoleForElasticLoadBalancing" || aws iam create-service-linked-role --aws-service-name "elasticloadbalancing.amazonaws.com"
#
#
# Installing eksctl
echo '============================================'
echo 'EKSCTL'
echo '============================================'
curl --silent --location "https://github.com/weaveworks/eksctl/releases/latest/download/eksctl_$(uname -s)_amd64.tar.gz" | tar xz -C /tmp
sudo mv -v /tmp/eksctl /usr/local/bin
eksctl completion bash >> ~/.bash_completion
. /etc/profile.d/bash_completion.sh
. ~/.bash_completion
#
#
# Installing kubectl
echo '============================================'
echo 'KUBECTL'
echo '============================================'
sudo curl --silent --location -o /usr/local/bin/kubectl https://amazon-eks.s3.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/1.17.11/2020-09-18/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl
#
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/kubectl
#
#
# Installing yq for yaml processing
echo 'yq() {
docker run --rm -i -v "${PWD}":/workdir mikefarah/yq yq "$@"
}' | tee -a ~/.bashrc && source ~/.bashrc
#
#
# Verifying the binaries are in the path and executable
for command in kubectl jq envsubst aws
do
which $command &>/dev/null && echo "$command in path" || echo "$command NOT FOUND"
done
#
#
# Enable kubectl bash_completion
kubectl completion bash >> ~/.bash_completion
. /etc/profile.d/bash_completion.sh
. ~/.bash_completion
#
#
# Set the AWS Load Balancer Controller version
echo 'export LBC_VERSION="v2.0.0"' >> ~/.bash_profile
. ~/.bash_profile
#
echo '============================================'
echo 'Helem'
echo '============================================'
curl -sSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/helm/helm/master/scripts/get-helm-3 | bash
helm version --short
helm repo add stable https://charts.helm.sh/stable
helm search repo stable
helm completion bash >> ~/.bash_completion
. /etc/profile.d/bash_completion.sh
. ~/.bash_completion
source <(helm completion bash)
#
echo 'eksctl version is' $(eksctl version)
echo 'kubectl version is' $(kubectl version --client --short)
7. How to create and import a SSH key
Before proceeding with how to create and import a Secure Shell Protocol (SSH) key which can be used to create a cluster and access a worker node in the Amazon EKS, I would like to point out that only a main developer for the Amazon EKS should create and import the SSH key once. The other developer can use the SSH key that is shared from the main developer. You should follow two steps to create and import the SSH key as follows.
- How to create the SSH key
You can easily create the SSH key as below.1 $ ssh-keygenGenerating public/private rsa key pair. Enter file in which to save the key (/home/ubuntu/.ssh/id_rsa): Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase): Enter same passphrase again: Your identification has been saved in /home/ubuntu/.ssh/id_rsa. Your public key has been saved in /home/ubuntu/.ssh/id_rsa.pub. The key fingerprint is: SHA256:R0r6qAcJ34PHBdS1m2ZrF2bgo+nUANwDPcECt0TUTvo ubuntu@ip-10-172-96-182 The key's randomart image is: +---[RSA 3072]----+ | .=B=.o. | | +o+B . | | +*+.+ | | . .+o= + | | o =.oS O + | | = =oEO = . | | o..= + . | | ..o . . | | .. . | +----[SHA256]-----+ - How to import the created SSH key
You can import the created SSH key as below. Please note that you can replace the vujade-eks with the name that you want. In this case, The vujade-eks is used as SSH key name. You can get more information AWS CLI Command Reference - import-key-pair in details.1 $ aws ec2 import-key-pair --key-name vujade-eks --public-key-material file://~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub{ "KeyName": "vujade-eks", "KeyFingerprint": "1f:51:ae:28:bf:89:e9:d8:1f:25:5d:37:2d:7d:b8:ca", "KeyPairId": "key-1g15s88175abcd1aa" } - How to import the shared SSH key to a new AWS Cloud9 instance
Please note that you must keep an original key which is located in ~/.aws/authorized_keys. If you lose the information, you cannot access the AWS Cloud9. Thus, you follow below instructions carefully to keep the original authorized key.- Copy the shared ~/.ssh/id_rsa.
- Copy the shared ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub.
- Add the key in the shared ~/.ssh/authorized_keys to the ~/.ssh/authorized_keys for the new AWS Cloud instance.
8. How to create an AWS KMS custom managed key (CMK)
Like creating and importing the SSH key in the Section 7. How to create and import a SSH key, only a main developer for the Amazon EKS should create a CMK once. The other developer can use the CMK that is shared from the main developer.
- How to create the CMK
You can crate the CMK as below. Please note that you can replace the vujade-eks with the name that you want. In this case, The vujade-eks is used as CMK key name. Please note that you can check your own account ID number from the result. In this case, the account ID is 123456789123.1 $ aws kms create-alias --alias-name alias/vujade-eks --target-key-id $(aws kms create-key --query KeyMetadata.Arn --output text) 2 $ export MASTER_ARN=$(aws kms describe-key --key-id alias/vujade-eks --query KeyMetadata.Arn --output text) 3 $ echo "export MASTER_ARN=${MASTER_ARN}" | tee -a ~/.bash_profileexport MASTER_ARN=arn:aws:kms:ap-northeast-2:123456789123:key/a0b1234c-de5f-6789-g01h-2i3456j789k0 - How to check the created CMK
You can check the created CMK by executing below command. You can get CMK key ID from the Section 8-1. How to create the CMK. In this case, the CMK key ID is a0b1234c-de5f-6789-g01h-2i3456j789k0.1 $ aws kms list-aliases --key-id a0b1234c-de5f-6789-g01h-2i3456j789k0{ "Aliases": [ { "AliasArn": "arn:aws:kms:ap-northeast-2:123456789123:alias/vujade-eks", "CreationDate": 1642430327.096, "AliasName": "alias/vujade-eks", "LastUpdatedDate": 1642430327.096, "TargetKeyId": "a0b1234c-de5f-6789-g01h-2i3456j789k0" } ] } - How to get the AWS account ID
You can also get the AWS account ID as follows.1 $ aws sts get-caller-identity --query Account --output text123456789123
9. How to resize the Elastic Block Storage (EBS) volume
You should resize the EBS of the Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) on the EC2 dashboard as shown in Fig. 5.
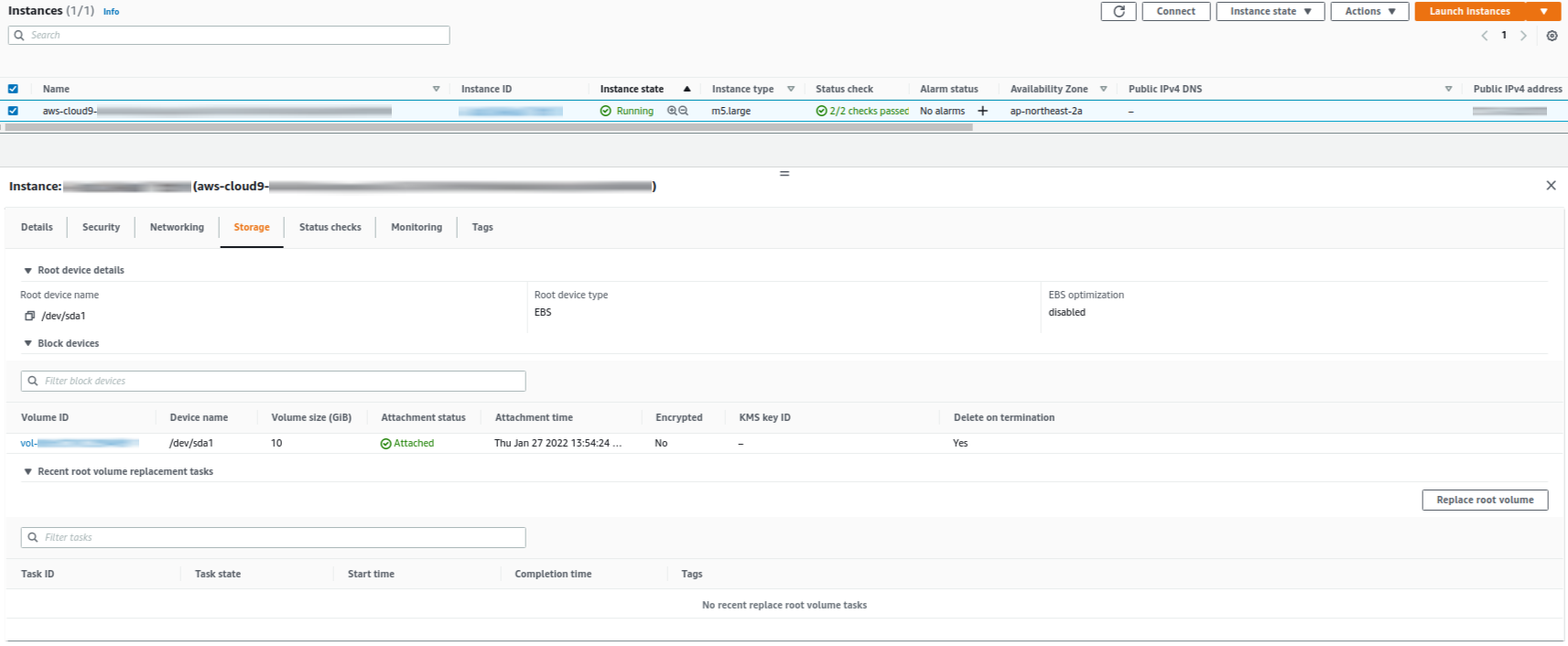
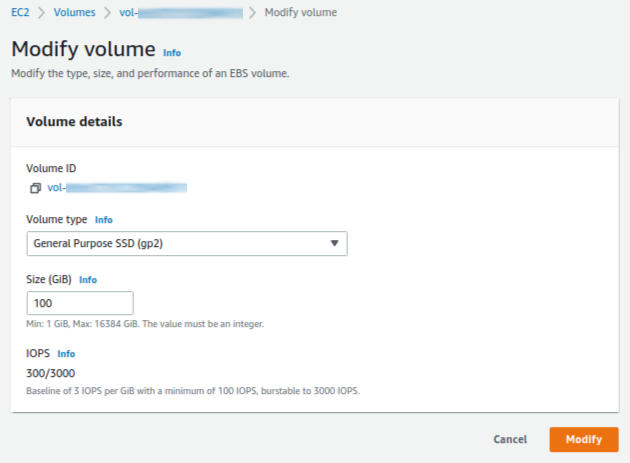
After you resize the EBS, you should follow below steps to apply the resized EBS. You can check the name of target disk of which size is resized volume. In this case, the name of target block device is nvme0n1.
1 $ lsblk
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
loop0 7:0 0 43.3M 1 loop /snap/snapd/14295
loop1 7:1 0 25M 1 loop /snap/amazon-ssm-agent/4046
loop2 7:2 0 99.4M 1 loop /snap/core/11993
loop3 7:3 0 55.5M 1 loop /snap/core18/2253
loop4 7:4 0 55.5M 1 loop /snap/core18/2284
loop5 7:5 0 43.4M 1 loop /snap/snapd/14549
loop6 7:6 0 110.5M 1 loop /snap/core/12603
loop7 7:7 0 4.7M 1 loop /snap/yq/1515
nvme0n1 259:0 0 100G 0 disk
└─nvme0n1p1 259:1 0 10G 0 part /
Then you can grow partition as below.
1 $ sudo growpart /dev/nvme0n1 1
CHANGED: partition=1 start=2048 old: size=20969439 end=20971487 new: size=209713119,end=209715167
You can resize the filesystem after checking the filesystem name. In this case, the filesystem name is /dev/nvme0n1p1.
1 $ df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
udev 3.8G 0 3.8G 0% /dev
tmpfs 767M 800K 766M 1% /run
/dev/nvme0n1p1 9.7G 9.0G 658M 94% /
tmpfs 3.8G 0 3.8G 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 5.0M 0 5.0M 0% /run/lock
tmpfs 3.8G 0 3.8G 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/loop0 44M 44M 0 100% /snap/snapd/14295
/dev/loop1 25M 25M 0 100% /snap/amazon-ssm-agent/4046
/dev/loop2 100M 100M 0 100% /snap/core/11993
/dev/loop3 56M 56M 0 100% /snap/core18/2253
tmpfs 767M 0 767M 0% /run/user/1000
/dev/loop4 56M 56M 0 100% /snap/core18/2284
/dev/loop5 44M 44M 0 100% /snap/snapd/14549
/dev/loop6 111M 111M 0 100% /snap/core/12603
/dev/loop7 4.8M 4.8M 0 100% /snap/yq/1515
1 $ sudo resize2fs /dev/nvme0n1p1
resize2fs 1.44.1 (24-Mar-2018)
Filesystem at /dev/nvme0n1p1 is mounted on /; on-line resizing required
old_desc_blocks = 2, new_desc_blocks = 13
The filesystem on /dev/nvme0n1p1 is now 26214139 (4k) blocks long.
Finally, you can check the resized EBS as below.
1 $ lsblk
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
loop0 7:0 0 43.3M 1 loop /snap/snapd/14295
loop1 7:1 0 25M 1 loop /snap/amazon-ssm-agent/4046
loop2 7:2 0 99.4M 1 loop /snap/core/11993
loop3 7:3 0 55.5M 1 loop /snap/core18/2253
loop4 7:4 0 55.5M 1 loop /snap/core18/2284
loop5 7:5 0 43.4M 1 loop /snap/snapd/14549
loop6 7:6 0 110.5M 1 loop /snap/core/12603
loop7 7:7 0 4.7M 1 loop /snap/yq/1515
nvme0n1 259:0 0 100G 0 disk
└─nvme0n1p1 259:1 0 100G 0 part /
1 $ df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
udev 3.8G 0 3.8G 0% /dev
tmpfs 767M 800K 766M 1% /run
/dev/nvme0n1p1 97G 9.0G 88G 10% /
tmpfs 3.8G 0 3.8G 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 5.0M 0 5.0M 0% /run/lock
tmpfs 3.8G 0 3.8G 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/loop0 44M 44M 0 100% /snap/snapd/14295
/dev/loop1 25M 25M 0 100% /snap/amazon-ssm-agent/4046
/dev/loop2 100M 100M 0 100% /snap/core/11993
/dev/loop3 56M 56M 0 100% /snap/core18/2253
tmpfs 767M 0 767M 0% /run/user/1000
/dev/loop4 56M 56M 0 100% /snap/core18/2284
/dev/loop5 44M 44M 0 100% /snap/snapd/14549
/dev/loop6 111M 111M 0 100% /snap/core/12603
/dev/loop7 4.8M 4.8M 0 100% /snap/yq/1515
10. How to fix error
1. Cannot access the AWS Cloud9 instance
The VPC must have a public subnet. (A subnet is public if its traffic is routed to an internet gateway.) If you’re using a public subnet, attach an internet gateway to the VPC so the SSM Agent for the instance can connect to Systems Manager. If you’re using a private subnet, allow the instance for the subnet to communicate with the internet by hosting a NAT gateway in a public subnet [8]. If you cannot access the AWS Cloud9 instance as shown in Fig. 6, you can check the subnet in the Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) - Section 7. How to set up a route table for the internet gateway.
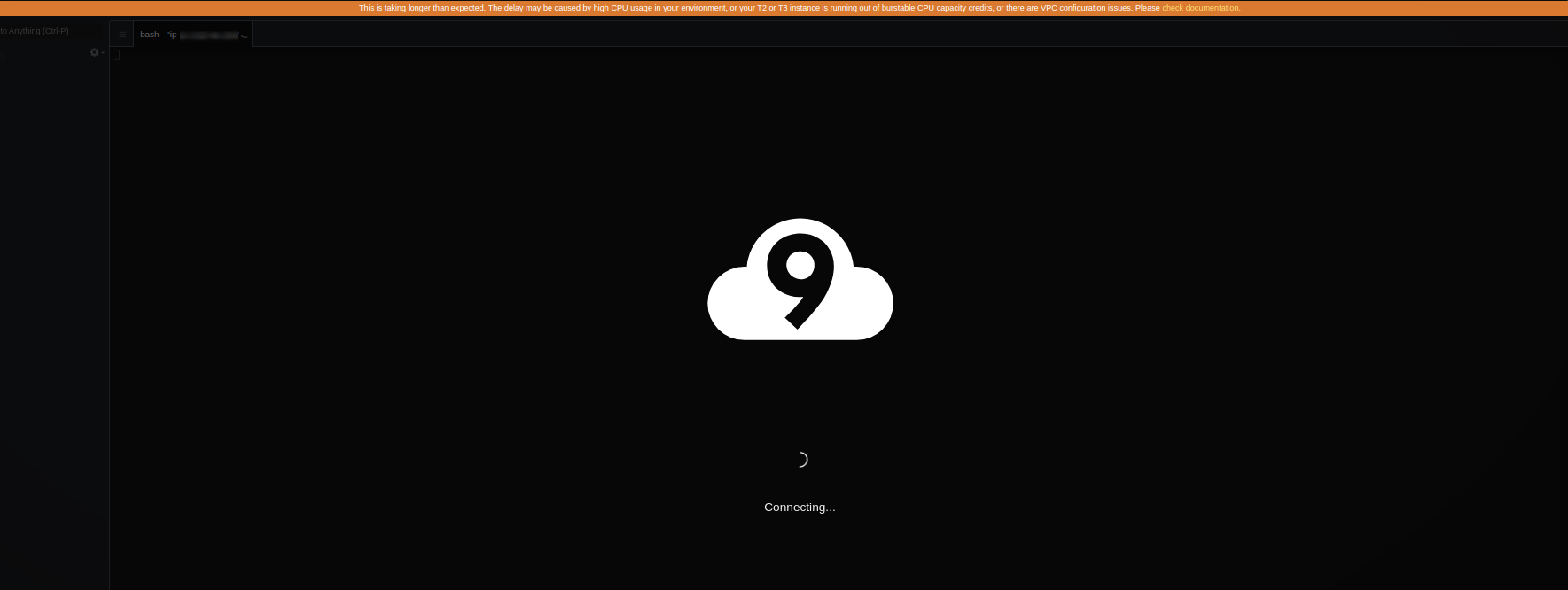
2. Cannot access the AWS Cloud9 instance
If you lose an original authorized key which is located in ~/.aws/authorized_keys, you can never access the AWS Cloud instance as shown in Fig. 7. In this case, I recommend you terminate the Cloud9 instance and create a new one. You can get more information in the Section 7. How to create and import a SSH key.
11. Reference
- Regions and Zones
- AWS Cloud9
- Update IAM settings for your workspace
- Ensure the ELB service role exists
- Prerequisites
- Install kubernetes tools
- Install HELM CLI
- Amazon VPC requirements for AWS Cloud9